Your task is to determine the Average Biomass yeild, Average Product yield and the Maximum specific growth rate from the plotting of the biomass concentration profile and product concentration profile of batch fermentation running at different initial glucose concentration from 80 g/L to 120 g/L.
Introduction
|
A glucose source and a microbe capable of producing ethanol are required in the fermentation process. Cellulosic crops, also known as energy crops, have a relatively lower cost per Joule of energy provided and therefore become a common source of glucose. Pretreated straw, in particular, is often used as the glucose source for ethanol production. Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a kind of yeast which is able to grow anaerobically on glucose and tolerate more than 15 wt% ethanol, is selected as the microorganism for fermentation.
The reactor used in ethanol production is a batch stirred-tank reactor made of stainless steel (Figure 2). The cooling jacket outside the vessel maintains the temperature inside the reactor at a certain range suitable for microbial growth. The impeller and baffle are required to improve mixing, since it is desirable to have a uniform distribution of temperature, pH, as well as cell, substrate and product concentration inside the vessel.
|
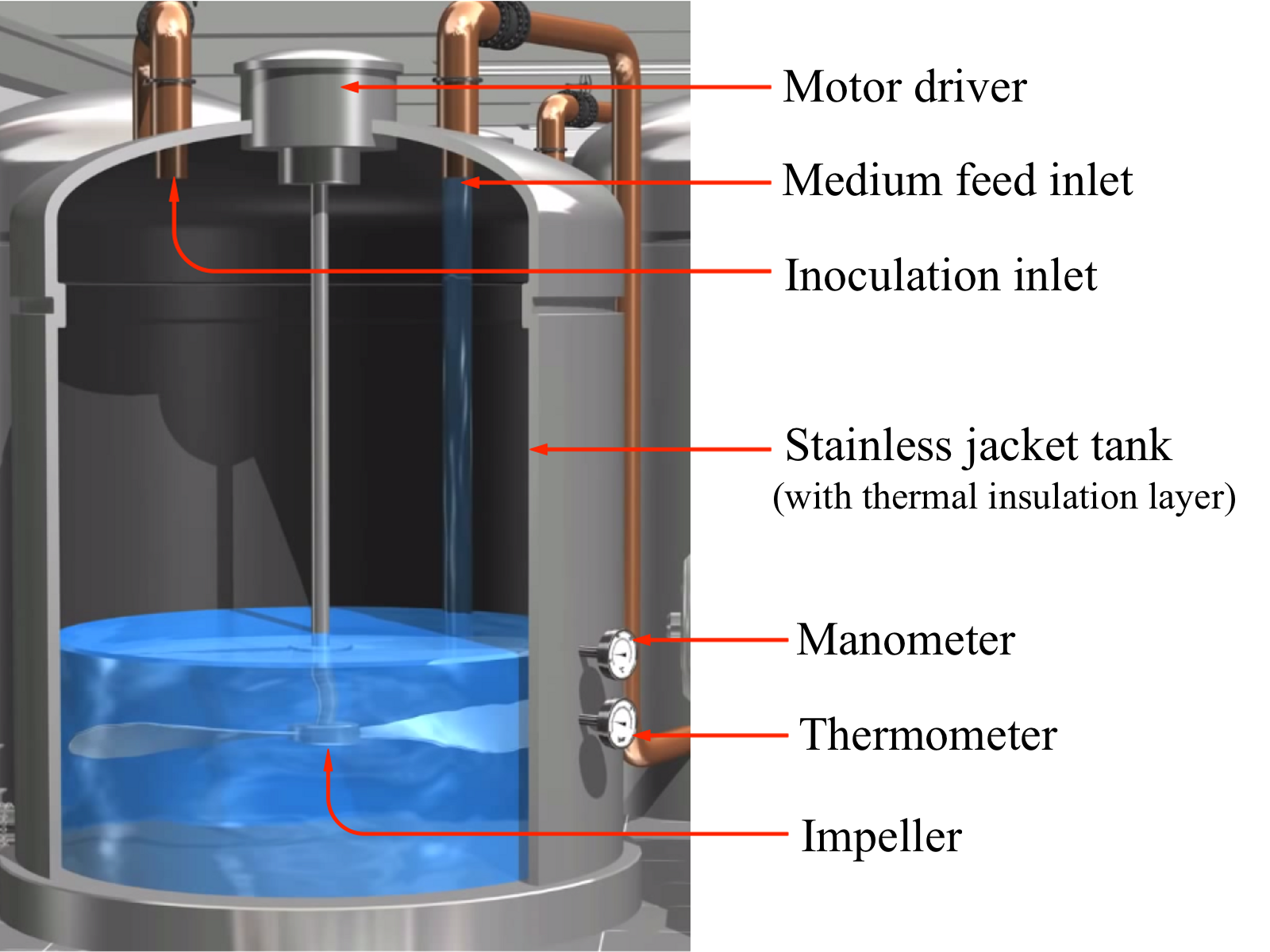
Fig 2. Stainless steel batch bioreactor
|
| Initial Glucose Concentration (g/L) |
| Time (h) | Glucose (S), g/L | Biomass (X), g/L | Ethanol (P), g/L |
|
|
||||||
| Biomass Yield (g Biomass / g Glucose): |
Product Yield (g Ethanol/ g Glucose): |
|||||
| Maximum Specific Growth Rate (g・h-2) |
|
|||||

Explanation for average biomass yield and average product yield calculation
The formula of average biomass yield and average product yield are as follows:
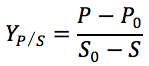 |
and | 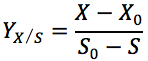 |
where S = substrate, P = product, X = biomsss, subscript "0" indicates initial condition.
For batch fermentation starting with 100 g/L glucose, the corresponding yields are as follows:
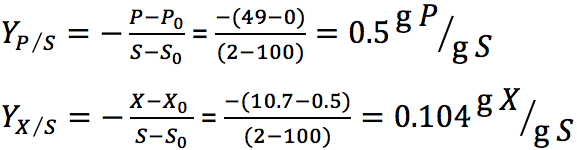

Explanation for specific growth rate calculation
Maximum specific growth rate is defined as the specific growth rate during exponential growth phase. The range of exponential growth rate can be identified by the linear region of logarithmic biomass concentration profile.
|
Biomass concentration before and after exponential growth phase are
X1 = 1.0g/L and X2 = 9.6g/L respectively. By equation of straight line, the specific growth rate can be found by calculate the slope of the linear region. 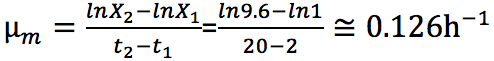 |